Introduction:
SAP Identity Access Governance (IAG) is a cloud-based solution that helps organizations to manage the lifecycle of user access and roles across SAP and non-SAP systems. It enables compliance with regulations, policies, and best practices for identity and access management (IAM).
Change management is a critical process for ensuring the success and stability of any IAM solution. It involves planning, testing, communicating and implementing changes in a controlled and coordinated manner. Change management helps to minimize risks, reduce errors and avoid disruptions to the business operations and user experience.
Types of changes in SAP IAG:
Changes in SAP IAG can be classified into two categories:
- Configuration Changes are changes that can be done through the SAP IAG user interface or the SAP Cloud Platform cockpit. They include settings, parameters, options, and features that can be adjusted or enabled by the administrator or the owner of the SAP IAG tenant. Configuration changes do not require coding or development skills.
- Customization Changes are changes that require coding or development skills. They include extensions, integrations, enhancements, and modifications that are done through the SAP Cloud Platform tools or the SAP IAG SDK. Customization changes may involve creating or modifying custom applications, services, APIs, UIs, or workflows.
Change Management Process in SAP IAG:
The change management process for SAP IAG consists of four phases: planning, testing, communicating, and implementing. Each phase has its own activities, roles, and responsibilities.
- Planning: This phase involves identifying the need, scope, impact, and benefits of the change. It also involves defining the objectives, requirements, resources, timeline, and risks of the change. The planning phase is led by the change owner, who is the person or the team that initiates and sponsors the change. The change owner should document the change request and get the approval from the relevant stakeholders, such as the business owners, the IT managers, the security officers, and the compliance auditors.
- Testing: This phase involves verifying the functionality, performance, quality and security of the change. It also involves validating the compatibility, interoperability, and compliance of the change with the existing systems and processes. The testing phase is led by the change developer, who is the person or the team that designs and develops the change. The change developer should follow the SAP IAG development guidelines and best practices and use the SAP Cloud Platform tools and environments for testing. The change developer should also document the test results and get the feedback from the change owner and the end users.
- Communicating: This phase involves informing and educating the stakeholders and the end users about the change. It also involves providing the necessary training, documentation, and support for the change. The communicating phase is led by the change communicator, who is the person or the team that handles the communication and the training activities. The change communicator should use the appropriate channels, methods, and materials for communicating the change, such as emails, newsletters, webinars, videos, manuals, or FAQs. The change communicator should also monitor and address the queries, issues, and feedback from the stakeholders and the end users.
- Implementing: This phase involves deploying and activating the change in the production environment. It also involves monitoring and evaluating the change after the implementation. The implementing phase is led by the change implementer, who is the person or the team that executes the change in the production environment. The change implementer should follow the SAP IAG deployment guidelines and best practices use the SAP Cloud Platform tools and environments for implementing. The change implementer should also document the implementation steps and outcomes and report any incidents or problems to the change owner and the change developer.
Change Logs:
SAP IAG change logs can be viewed through the below reports.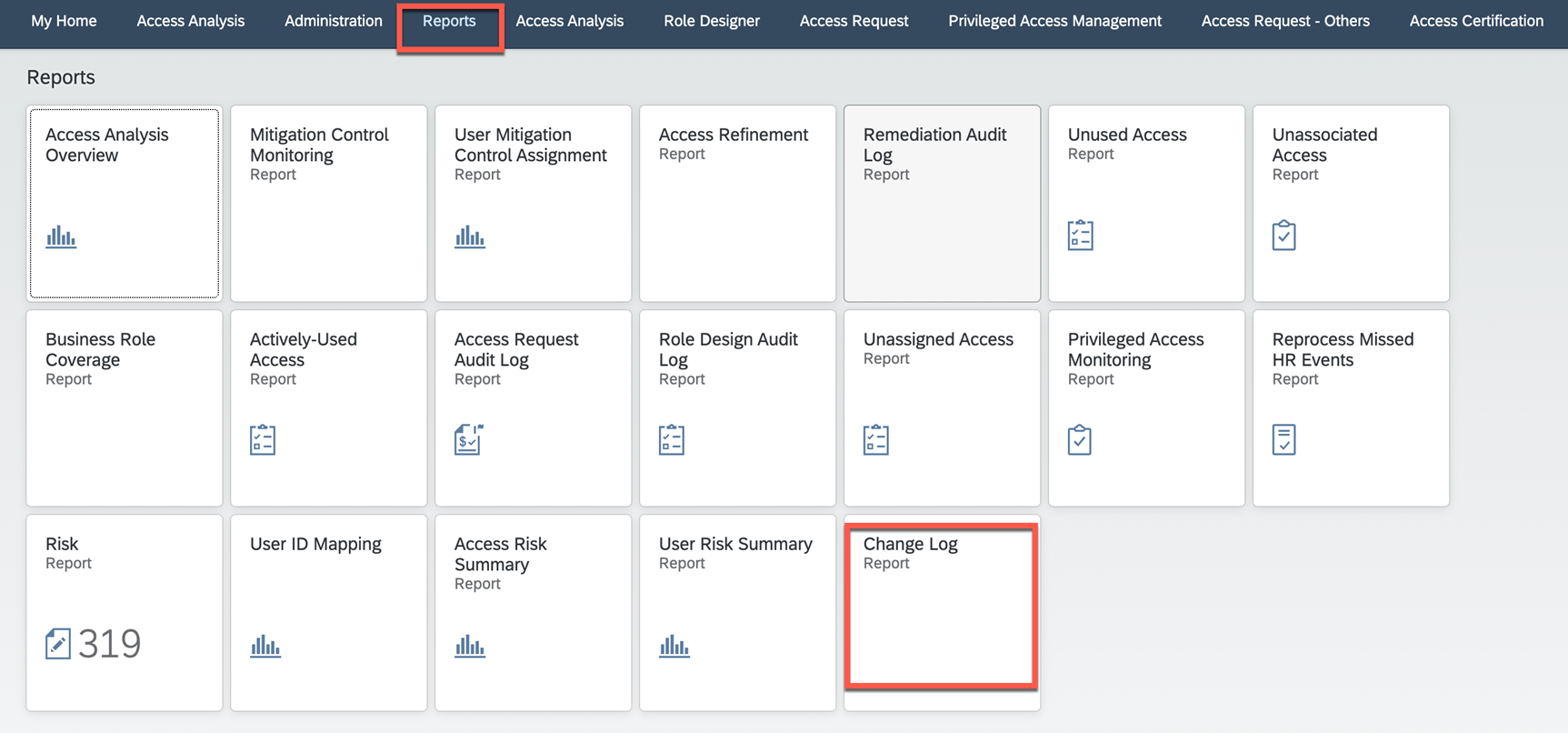
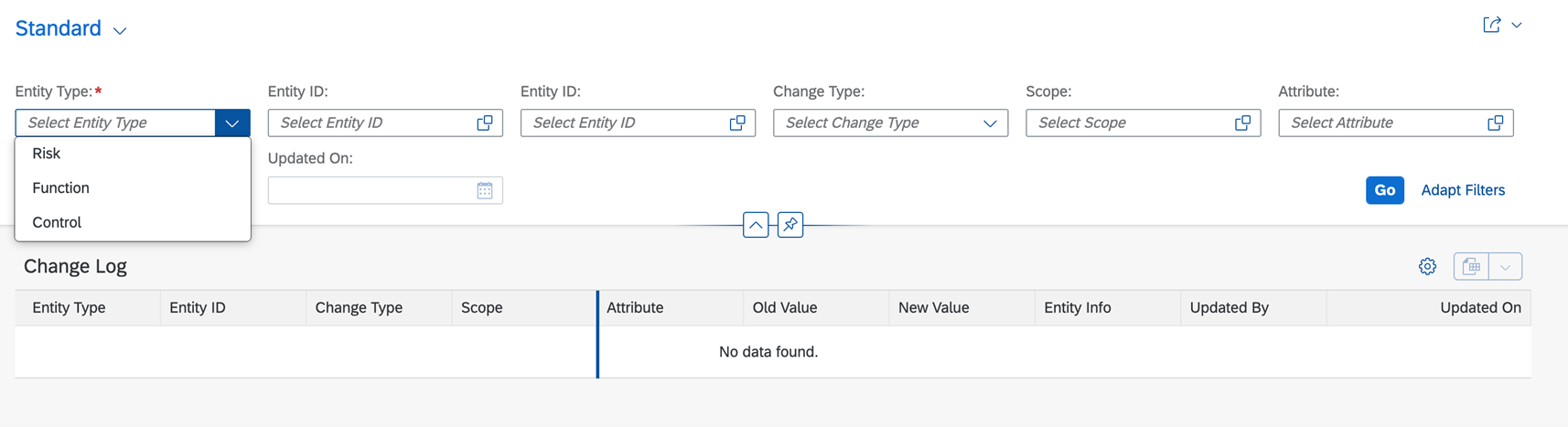
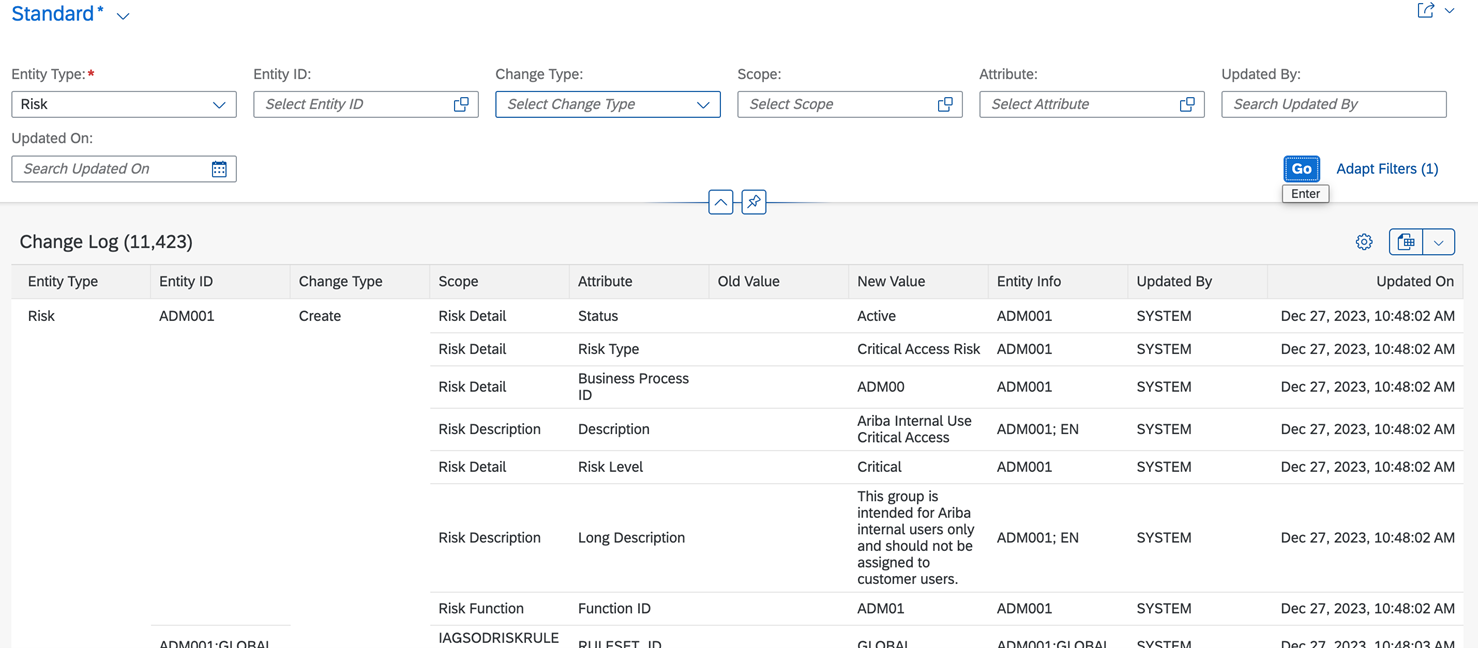
Following options are available in change log reporting.
Master Data –
- Changes to Controls
- Changes to Risk
- Changes to Functions
Change Type –
- Create
- Update
- Delete
Conclusion:
SAP IAG change management is a vital process for ensuring the success and stability of the SAP IAG solution. It helps to align the changes with the business needs and goals and to ensure the quality and security of the changes. By following the change management process and the roles and responsibilities, the SAP IAG customers and partners can manage the changes in a controlled and coordinated manner and achieve the desired results and benefits.

